Mazda 3 Service Manual: Starter Inspection [Mzr 2.0, Mzr 2.5]
On-vehicle Inspection
1. Verify that the battery is fully charged.
2. The starter is normal if it rotates smoothly and without any noise when the engine is cranked.
-
If the starter does not operate, inspect the following:
-
Remove the starter, and inspect the starter unit.
-
Inspect the related wiring harnesses, the ignition switch, and the transaxle range switch (ATX) or starter interlock switch (MTX).
No-load Test
1. Verify that the battery is fully charged.
2. Connect the starter, battery, and a tester as shown in the figure.
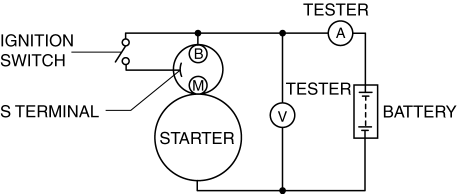
3. Operate the starter and verify that it rotates smoothly.
-
If the starter does not rotate smoothly, inspect the starter unit.
4. Measure the voltage and current while the starter is operating.
-
If not within specification, replace the starter.
-
Starter no-load test voltage
-
11 V
-
Starter no-load test current
-
MZR 2.0 : 95 A or less
-
MZR 2.5 : 90 A or less
Magnetic Switch Operation Inspection
Pull-out test
NOTE:
-
Depending on the battery charge condition, the starter motor pinion may rotate while in an extended state. This is due to current flowing to the starter motor through the pull-in coil to turn the starter motor, and does not indicate an abnormality.
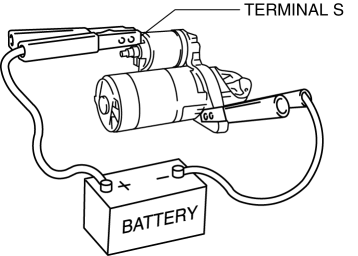
1. Verify that the starter motor pinion is extended while battery positive voltage is connected to terminal S and the starter body is grounded.
-
If the starter motor pinion is not extended, repair or replace the starter.
Return test
1. Disconnect the motor wire from terminal M.
2. Connect battery positive voltage to terminal M and ground the starter body.
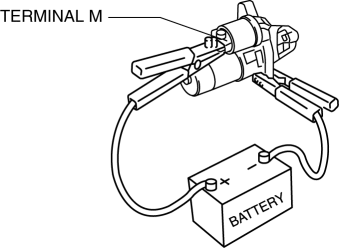
3. Pull out the drive pinion with a screwdriver. Verify that it returns to its original position when released.
-
If it does not return, repair or replace the starter.
Pinion Gap Inspection
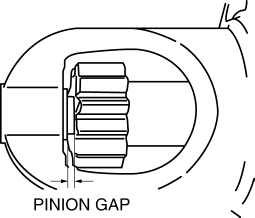
1. Pull out the drive pinion with the battery positive voltage connected to terminal S and the starter body grounded.

CAUTION:
-
Applying power for more than 10 s can damage the starter. Do not apply power for more than 10 s.
2. Measure the pinion gap while the drive pinion is extended.
-
If not as specified, adjust with an adjustment washer (between drive housing front cover and magnetic switch).
-
Starter pinion gap
-
0.5—2.0 mm {0.02—0.07 in}
Starter Inner Parts Inspection
Armature
1. Verify that there is no continuity between the commutator and the core at each segment using a tester.
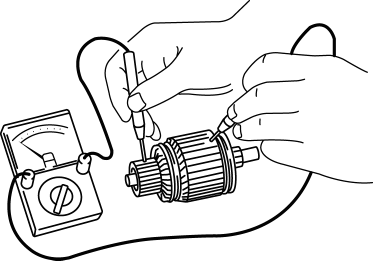
-
If there is continuity, replace the armature.
2. Verify that there is no continuity between the commutator and the shaft using a tester.
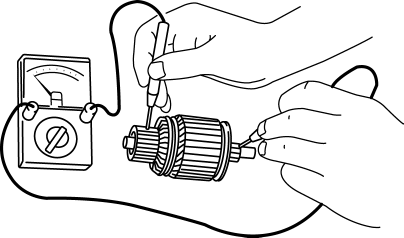
-
If there is continuity, replace the armature.
3. Place the armature on V–blocks, and measure the runout using a dial indicator.
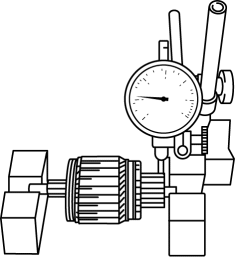
-
If not within specification, replace the armature.
-
Starter armature runout
-
0.1 mm {0.004 in} max.
4. Measure the commutator diameter.
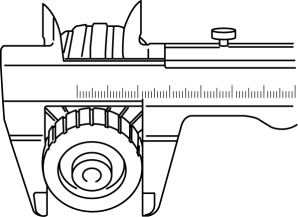
-
If not within the minimum specification, replace the armature.
-
Starter commutator diameter
-
Standard: 29.4 mm {1.16 in}
-
Minimum: 28.8 mm {1.13 in}
5. Measure the segment groove depth of the commutator.
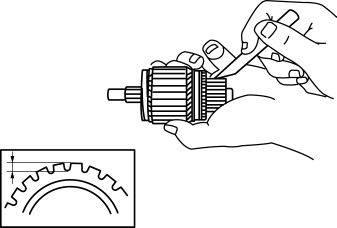
-
If not within the minimum specification, undercut the grooves to the standard depth.
-
Segment groove depth of starter commutator
-
Standard: 0.5 mm {0.02 in}
-
Minimum: 0.2 mm {0.008 in}
Magnetic switch
1. Inspect for continuity between terminals S and M using a tester.
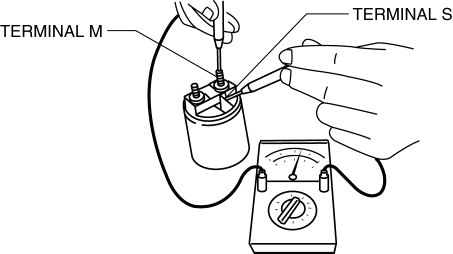
-
If there is no continuity, replace the magnetic switch.
2. Inspect for continuity between terminal S and the body using a tester.
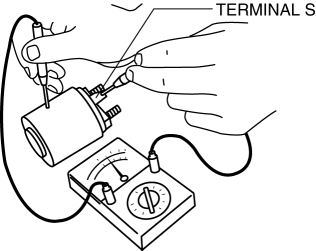
-
If there is no continuity, replace the magnetic switch.
3. Verify that there is no continuity between terminals M and B using a tester.
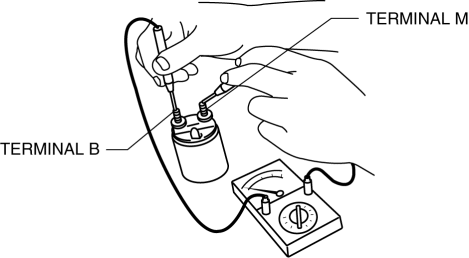
-
If there is continuity, replace the magnetic switch.
Brush and brush holder
1. Verify that there is no continuity between each insulated brush and plate using a tester.
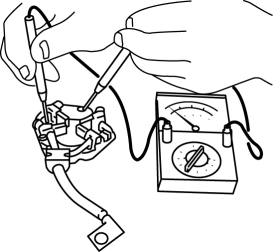
-
If there is continuity, replace the brush holder.
2. Measure the brush length.
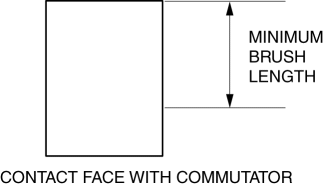
-
If any brush is worn almost to or beyond the minimum specification, replace all of the brushes.
-
Starter brush length
-
Standard: 12.3 mm {0.484 in}
-
Minimum: 5.5 mm {0.22 in}
3. Measure the brush spring force using a spring balance.
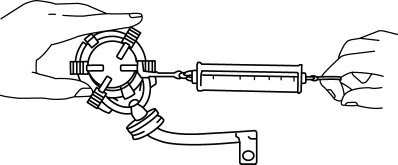
-
If not within the minimum specification, replace the brush and brush holder component.
-
Starter brush spring force
-
Standard: 15.1—20.4 N {1.54—2.08 kgf, 3.40—4.58 lbf}
-
Minimum: 2.75 N {0.280 kgf, 0.618 lbf}
 Starter Disassembly/Assembly [Mzr 2.0, Mzr 2.5]
Starter Disassembly/Assembly [Mzr 2.0, Mzr 2.5]
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
2. Assemble in the reverse order of disassembly.
1
Magnetic switch
2
Adjustment washer
...
 Starter Interlock Switch Inspection [Mzr 2.0, Mzr 2.5]
Starter Interlock Switch Inspection [Mzr 2.0, Mzr 2.5]
CAUTION:
Do not reuse the starter interlock switch if it is removed from the vehicle
even once. Replace with a new starter interlock switch when installing.
1. Remove the battery cove ...
Other materials:
How to Use the Bluetooth ® Audio System
Switching to Bluetooth ® audio mode
To listen to music or voice audio recorded to a Bluetooth ® audio device,
switch to the
Bluetooth ® audio mode to operate the audio device using the audio system
control panel.
Any Bluetooth ® audio device must be paired to the vehicle's Bluetooth ® unit ...
Front Bumper Removal/Installation
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable..
2. Remove the screw A and fasteners B.
3. Remove the screws C.
4. Remove the bolts D.
5. Remove the fasteners E, screw F and fastener G.
6. Pull the front bumper in the direction of the arrow in the order of (1), (2)
and (3), the ...
Air Intake Actuator Removal/Installation [Manual Air Conditioner]
1. Set the air intake mode to FRESH.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable..
3. Remove the following parts:
a. Front scuff plate (Passenger-side).
b. Front side trim (Passenger-side).
c. Dashboard under cover.
d. Glove compartment.
e. Lower panel (Passenger-side).
f. Shower duct ( ...
